type = “what”?
One great thing about R is that has a wide diversity of packages written by many different people of many different viewpoints on how software should be designed. However, this does tend to bite us periodically.
When I teach newcomers about R and predictive modeling, I have a slide that illustrates one of the weaknesses of this system: heterogeneous interfaces. If you are building a classification model and want to generate class probabilities for new samples, the syntax can be… diverse. Here is a sample of syntax for different models:
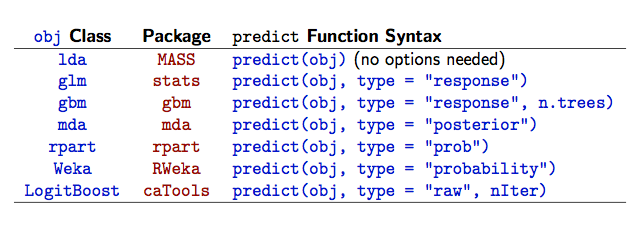
That’s a lot of minutia to remember. I did a quick and dirty census of all the classification models used by caret to quantify the variability in this particular syntax. The train utilizes 64 different models that can produce class probabilities. Of these, many were from the same package. For example, both nnet and multinom are in the nnet package and probably should not count twice since the latter is a wrapper for the former. As another example, the RWeka packages has at least six functions that all use probability as the value for type.
For this reason, I cooked the numbers down to one value of type per package (using majority vote if there was more than one). There were 40 different packages once these redundancies were eliminated. Here is a histogram of the type values for calculating probabilities:
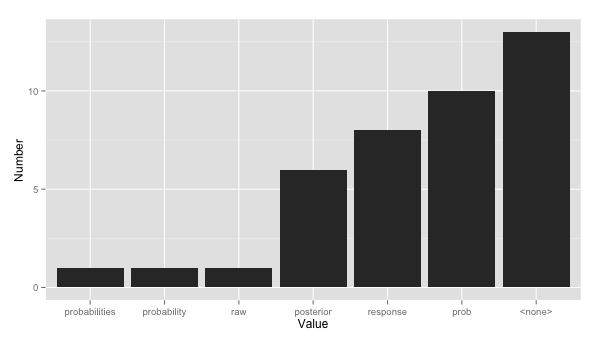 The most frequent situation is no
The most frequent situation is no type value at all. For example, the lda package automatically generated predicted classes and posterior probabilities without requiring the user to specify anything. There were a handful of cases where the class did not have a predict method to generate class probabilities (e.g. party and pamr) and these also counted as “none”.
For those of us that use R to create predictive models on a day-to-day basis, this is a lot of detail to remember (especially if we want to try different models). This is one of the reasons I created caret; it has a unified interface to models that eliminates the need to remember the name of the function, the value of type and any other arguments. In case you are wondering, I chose `type = “prob”’.
(This article was originally posted at http://appliedpredictivemodeling.com)